Arthrosis is a disease characterized by gradual destruction of the community due to the development of dystrophic changes in tissues.According to whom, every tenth resident of the planet is facing this problem.After 50 years, the risk of disease is about 30%, and up to 70 years reaches 80-90%.
General information
Arthrosis is a chronic, long-border process that affects not only compounds.As progressing, dystrophic and degenerative changes are also an amazing auxiliary apparatus.In the process, the patient is facing inflammation of cartilage and bone tissue, capsules of the wrist and periusmanian bags, as well as muscles, ligaments and subcutaneous tissues dealing with them.
Regardless of the localization, the pathological process passes in accordance with one scheme.First, in the thickness of the fabric, the balance between the growth process and the destruction of the cartilage is disturbed, and the balance shifts in favor of dystrophy and reverse development (degeneration).At the moment, changes in the invisible for the eye in the cartilage microstructure, which leads to his condition and shooting.
As the disease advances, the wrist loses elasticity and becomes thicker.This reduces its ability to be depreciated, the tissue damage rate is constantly increasing due to vibrations and microtrows during the movement.The Thing of the Cartivlation layer causes the active growth of bone structures, as a result whose spikes and pigs appear on the smooth surface of the compound - osteoarthrosis is developed.Movements become all limited and painful.Muscle cramps are developed that surround the affected surfaces, which worsens the pain and deforms the limb.
Stages of the disease
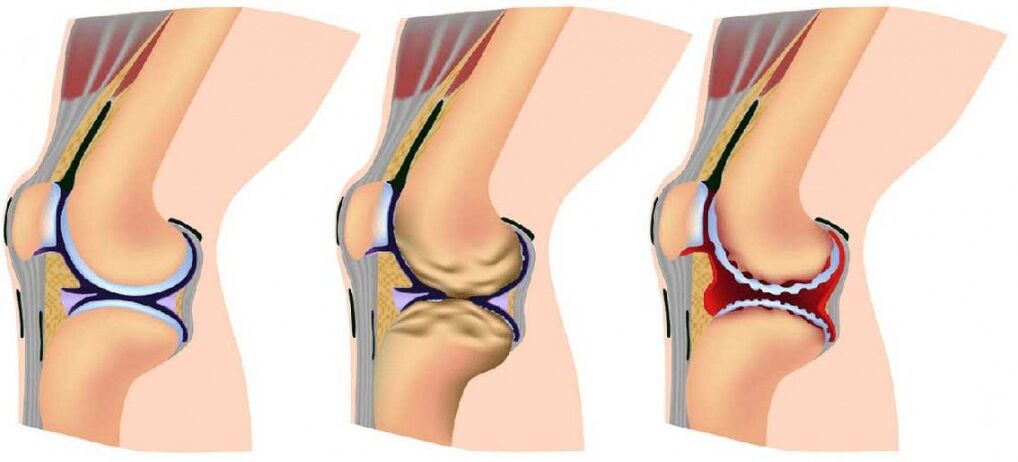
The arthrosis of joints develops gradually and in the process of three consecutive phases that determine the severity of the disease:
- Phase 1: The pathology is not revealed on X -Ray or ultrasound, but destruction processes have already been initiated;The composition of shared fluid changes, as a result that the tissues obtained less than nutrients and become more sensitive;Increased load in the area of damage causes inflammation (arthritis) and pain;
- The second phase is characterized by actively destroying fabric for cartilage, and bone spikes and growth appear along the edges of the common platform (area of contact area);At this point, the pain becomes known, and inflammatory processes go stronger or weaker;The breeds associated with muscle joints are periodically recorded;
- Phase 3: Areas of destruction affect the almost entire surface of the cartilage, a common platform is deformed, the injured limb deviates from its axis;The amount of movement is reduced, and the ligaments weaken and become short.
Some experts also differ the IV phase of arthrosis development.It is characterized by almost complete relation to the compound.
Types
Depending on the cause of the disease, the primary and secondary arthrosis are included.In the first case, pathology appears independently against the background of the comprehensive effect of predisposition factors.The secondary shape is the result of other diseases and is divided into the following groups:
- Damage to joints that occurred due to metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases (gout, diabetes melitus, acromegaly, hyperparatiroidism);
- Destruction associated with innate pathologies (Pedget's disease, innate lip dislocation, scoliosis, hemophilia, etc.);
- Post -Traumatic arthrosis, which originated with the background of fractures, cracks, necrotic processes or surgical operations, as well as created due to the characteristics of the profession.
The most on request is the classification of osteoarthritis, depending on the localization of the pathological procedure:
- Gonartrosis: Knee lesion, one of the varieties of which is pallet - pallet arthrosis - destruction of the wrist between the femur and patle;
- Arthrosis Joint Ankle: occurs on the background of a large load and frequent injuries;
- Arthrosis of foot joints: The thumb usually suffers on the foot with the foot;The defeat develops against the background of gihov or valgus deformation;
- Arthrosis shoulders is characterized by shoulder damage and are often found in youth than the background of increased physical activity (drivers, athletes, builders);
- Coxartrosis: Damage to the hip joint;Perhaps one - a lily and bilateral and is one of the frequent causes of disability in people over 50;
- Vertebral arthrosis: Destruction of cartilage discs between vertebral, most often affects cervix and lumbar spine;
- Brush joint arthrosis: Finger joints are most often affected, pathologies are especially susceptible to women in menopause;
- Temporomandibular compound arthrosis: It is quite rare, most often against the background of chronic inflammation due to bite disorders or irregular prosthetics;
- Arthrosis of the shared elbow: a rare form of disease, most often associated with the injuries of this area.
Reasons for development
The main factor in the development of arthrosis is the mismatch between the test and the joint capacity of the joint to withstand this burden.Acute or chronic, this process inevitably leads to tissue destruction.
A list of causes that increase the risk of arthrosis of any localization includes:
- heredity;
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes);
- Injuries of articulated apparatus: bruises, dislocations, fractures or cracks of bones within a common bag, full or partial ligament breaks that penetrate the wounds;
- Regularly increased shared load associated with the profession;
- obesity;
- hypothermia;
- Intended inflammatory joint diseases: acute arthritis, tuberculosis, etc.;
- Blood diseases in which bleeders often occur in the wrist (hemophilia);
- sharp changes in hormone background (pregnancy, menopause);
- Local circulator disorders related to atherosclerosis, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, etc.;
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, system lupus erythematosus, etc.);
- Binding tissue diplay (congenital pathology, accompanied, including excessive joint mobility);
- Congenital pathology of muscle-bone system (straight legs, dysplasia or innate hip joint dislocations, etc.);
- Age for more than 45-50 years (increasing risk is related to the fall of collagen synthesis);
- Osteoporosis (vacuum bones);
- Chronic body intoxication (including heavy metal, drugs, alcohols);
- Surgical interventions on the joints.
Symptoms
The symptoms of arthrosis practically independent of its cause and localization, because changes in the joints are going according to the same scenario.The disease gradually develops and starts manifesting, but when cartilage is quite severely damaged.
One of the first signs of dysfunction is crumb in the problem area during the movement.It usually occurs when the knee or shoulder is damaged.At the same time, a person can feel a slight decline in mobility after prolonged inactivity, for example, in the morning.
When asked which symptoms appeared with arthrosis, most patients first call pain.At first, insignificant and weak, it gradually gains strength, preventing it normally moves.Depending on the phase and localization of pathology, a person can feel:
- Starting pain: occur during the first movements after the extensive inactivity of the compound and are associated with formation on the surface of the crunchal thin film from the destroyed fabric;After the beginning of the paper, film changes and discomfort disappears;
- Pain with prolonged physical exertion (standing, walking, running, etc.): They appear due to the reduction of the striking joint properties;
- Time pain: caused by low temperature, moisture, atmospheric pressure changes;
- Night pain: associated with venous stagnation and increased blood pressure inside the bones;
- Articulated blockade: sharp, severe pain associated with breach of pieces of cartilage or bone located in the articulated cavity.
As the arthrosis is developing, symptoms become more noticeable, the patient records the following characters:
- increasing the entire stiffness;
- strengthening and increasing the duration of pain;
- Mobility reduction;
- Common deformation due to bone growth;
- Deformation of bones and surrounding tissues: The process is well noticeable in the limbs and fingers with hands, which become noticeably curved.
When the inflammation is attached, the affected area of swollen, blush and becomes hot on the touch.Pressing her causes a sharp increase in pain.

Analyzes and diagnostics
Arthrosis diagnostics deals with an orthopedic doctor.He conducts a detailed study of the patient for identifying complaints and anamnesis.The doctor is in detail of the time the first signs and speed of their development, injuries and diseases, the presence of similar problems in relatives.
The general blood test allows you to identify the inflammatory process, which often tracks arthrosis.
The main method of diagnosis is radiography.The following characters are clearly visualized in the figure:
- narrowing a common gap;
- Contact change contours Contacts;
- disturbed bone structure in the affected area;
- Bone growth (osteofiti);
- curvature of the axis or finger axes;
- Joint subbruxation.
For more detailed diagnostics, they can be prescribed:
- Computer Tomography (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Wrist ultrasound;
- Arthroscopy (internal examination of the common cavity using a camera introduced through a small piercing);
- Scintigraphy (assessment of the state of bones and metabolism in the introduction of radio farmerships).
In case of doubt in the secondary nature of the disease, appropriate tests and consultations of narrow experts are prescribed.
Treatment Arthrosis Joints
The selection of methodologies for treatment arthrosis joints depends on the cause of the disease, its phases and symptoms.In the Arsenal of the doctor there are:
- Drugs;
- Treatment for an unsocial;
- Surgical methods.
In addition, the patient needs to be strictly watched by nutrition and adapt his way of life to reduce additional joint damage.
Medicine treatment
The appointment of arthrosis drugs follows two main goals:
- displacement of pain and inflammation;
- Restoration of the cartilage fabric or, at least, stop further degeneration.
To facilitate the patient's state, various types of medications are used:
- not -steroidal anti -infalmator drugs in the form of tablets, injections, fats or candles;They relieve pain and inflammation well;
- Hormones (corticosteroids): shown in strong pain and are most often introduced directly into the articulated cavity;
- Other analgesics, for example, antispasodic procedure: help reduce the levels of pain with relaxing muscles;
It is important to remember: all types of painkillers are used only to facilitate the state of the patient.They do not affect the state of cartilage, and with extended use accelerate its destruction and cause serious side effects.
Main preparations for joint renewal today are hondroprotectors.They contribute to saturating cartilage with nutrients, stop the monument and start the cell growth processes.Funds have an effect only at an early and average phase of disease development and are subject to regular long-term use.
Preparations that improve microcirculation in tissues and anti -menings help improve the performance of hondroprotects.The first provides a good offer of affected area with oxygen and nutrients, and the latter slows down the tissue destruction processes.
Selecting certain medications, their dose and administration mode deals with a doctor.
Treatment of the heartless
Treatment that an unsocial includes the following methods:
- Physiotherapy:
- Shock therapy: destroys bone growth and encourages blood circulation due to ultrasound effects;
- Automated electromitumulation: exposure to electrical impulses to encourage muscle contraction;
- Ultrafonaphore: Ultrasound performance in combination using drugs;
- Ozonotherapy: Introduction of a special gas mixture into a shared capsule;
- Physical education of physiotherapy;
- Mechoterapy: Exercise therapy using simulators;
- Common traffic to reduce cargo;
- Massage.
Surgical treatment
The help of a surgeon is usually needed on the difficult stages of the disease.Depending on the localization of the pathological procedure and the degree of lesion, it can be prescribed:
- Breakthrough: punching joint with the removal of part of the liquid and, according to indication, application of medicines;
- Corrective osteotomy: Removing part of the bone, followed by fixing from a different angle to remove the load from the joint;
- EndoProsthetics: Replacement of damaged compound in prosthesis;Used in extremely neglected cases.
Arthrosis in children
Arthrosis is considered a disease of older people, but can also be found in children.The most common cause of pathology is:
- Congenital pathology of connective tissue;
- Heavy injuries;
- heredity;
- Metabolic disorders and work of internal excretion gland;
- Orthopedic disorders (flat feet, scoliosis, etc.);
- Excess weight.
Children's arthrosis is rarely accompanied by pronounced symptoms: pain aches, and practically no stiffness and limit of function.Monoatic changes are revealed to X -Ray, MRI and ultrasound.The same products as adults are used in the process of treatment.The maximum attention is paid to exercise therapy and physiotherapy, because they are especially efficient in the young age.Without treatment, the disease sooner or later passes into an advanced phase with a complete loss of mobility.
Diet
Diet is one of the most important factors in the treatment of arthrosis.In the presence of excess weight, it is necessary to reduce it to reduce the load on the joints.In this case, a balanced diet with a lack of calories is prescribed.Regardless of the body mass index, doctors recommend completely leaving:
- Fast carbohydrates (sugar, desserts, flour);
- alcohol;
- Spices;
- legumes;
- Strong tea and coffee;
- Excessively greasy and sharp meals.
Canned and outlets are not excluded, but are significantly limited, as well as salt.The ideal nutrition for osteoarthritis includes:
- Low varieties of meat;
- fish and seafood;
- eggs;
- Dairy products;
- Oil oil and olives;
- vegetables and fruits, large amount of greenery;
- Moderate cereals, tough-awrep pasta;
- Products with high collagen content (jelly, pour, want).
Prevention
Arthrosis is easier to warn than to treat.For the maintenance of common health for many years, it is recommended:
- lead an active way of life;
- regularly exercise and visit the pool;
- Eat correctly, use the omega-3 and collagen enough;
- prevent passing from BMI;
- Wear comfortable shoes.
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, regular undergoing spa treatment is recommended, as well as exclude professional risk factors: long-term stays on their feet, lifting strength, vibration.
Consequences and complications
Arthrosis is progressing very slowly.When performing a medical prescription, its immediate slows significantly, allows you to maintain articulated mobility much longer.Unregorous consequences are developed without treatment:
- A deformation in the joint;
- Reducing mobility to complete loss (ankylose);
- Shortening of limbs (with knee or thigh compound);
- Deformation of bones, curvature of limbs and fingers.
Forecast
The forecast for arthrosis depends on the form of disease, a degree and quality of treatment.Pathology is one of the frequent causes of disability, and in advanced cases, the ability to move and self-service.In heavy forms of damage to the knee and hook joints, the patient receives the first or other group for people with disabilities (depending on the phase and the scope of damage).